If you’re active on TikTok, you may have encountered videos showcasing the hair cracking trend, where individuals pull on their hair to elicit a popping sensation in their scalp. This practice is purported to relieve scalp tension and alleviate migraines, but does it actually work? Let’s dive into the facts.
What Is Hair Cracking?
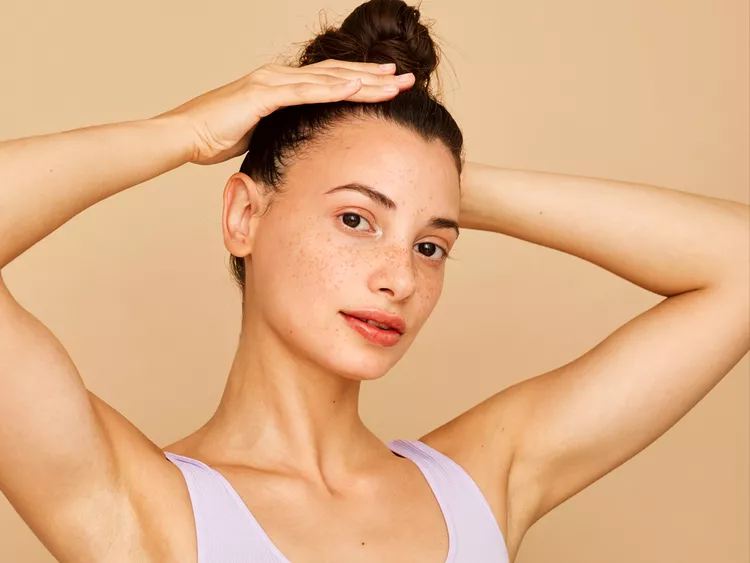
Hair cracking, also known as scalp popping, involves pulling rapidly on sections of hair to create a popping sensation in the scalp. The sensation occurs when the scalp separates from a layer of fibrous connective tissue called the galea aponeurotica. While popular on TikTok, dermatologists remain skeptical about its efficacy.
Is Hair Cracking Safe?
Hair cracking poses various risks, including traction alopecia, a form of hair loss caused by repeated hair pulling. This practice can damage hair follicles, leading to inflammation and permanent hair loss. Additionally, hair cracking can break hair strands or tear the skin, potentially worsening scalp health and inflammation.
Alternatives to Hair Cracking
Instead of hair cracking, consider gentle massage techniques to relieve tension in the temples, neck, and shoulders. For migraine relief, modify your environment to reduce sensory stimuli and apply cold or warm compresses. Consulting with a certified neurologist can provide further guidance on managing headaches and scalp tension.
The Final Takeaway
Hair cracking lacks scientific evidence to support its purported benefits and carries significant risks. Traction alopecia and scalp inflammation are potential consequences of this trend. Pursuing safer, evidence-based alternatives is advisable for managing headaches and scalp tension.
In summary, while hair cracking may seem appealing, its risks outweigh any potential benefits. Prioritize safe and effective methods for addressing scalp tension and headaches, and consult healthcare professionals for personalized guidance.




Comments are closed.